Hearing a lot about TB in Alaska? What do you need to know?
• Alaska and Hawaii have had the highest annual rates of tuberculosis (TB) in the US for many years.
• TB control continues to be a top priority for the Division of Public Health – Here is #Alaska’s TB website https://dhss.alaska.gov/dph/Epi/id/Pages/TB/providers.aspx. More on TB can be found here: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/default.htm
• TB is not evenly distributed around the state, some regions have many cases, others regions have very few cases – here is the 2020 summary brief: https://dhss.alaska.gov/.../TB/2020%20AK%20TB%20Summary.pdf
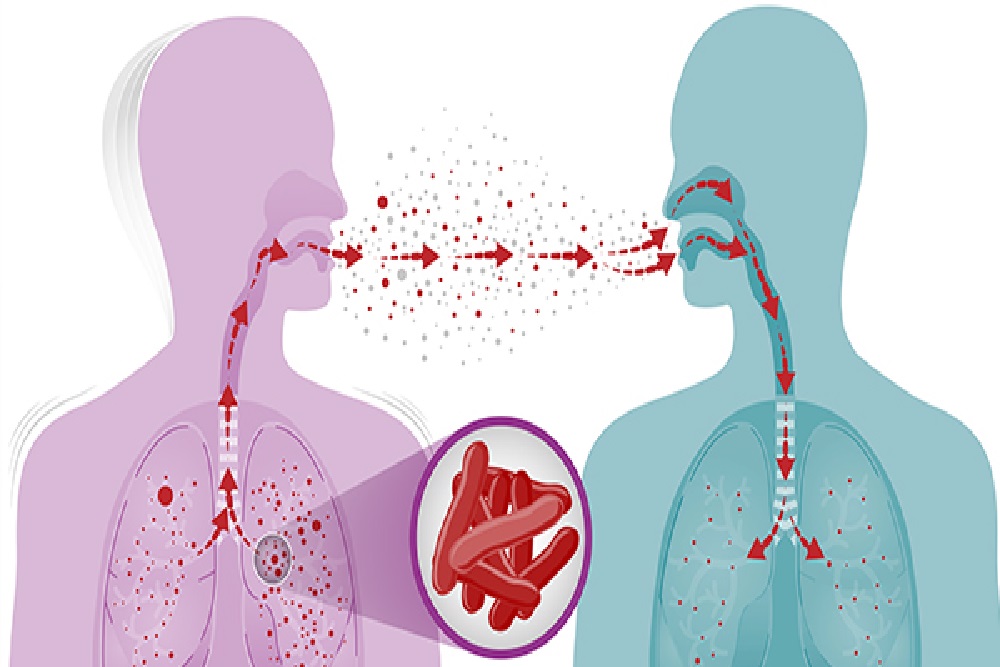
• Most people who are infected with the TB bacteria have latent TB, which means that they are asymptomatic and not infectious to others. Latent TB can be treated to prevent active TB, which can make people ill and is transmissible from person to person. https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/howtbspreads.htm
• About 5-10% of people with latent TB who do not receive treatment will at some point develop active TB in their lifetime
• The CDC, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the United States Preventive Services Task Force, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and TB experts in Alaska have all recommended against universal screening for TB in general as it is low-yield, ineffective use of resources, and may result in high numbers of false positives. Instead of universal screening, targeted screening is recommended, as most children do not have risk factors for TB. This is why the process for a regulations change started in 2013 with significant stakeholder engagement. See
https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/64/2/e1/2629583 , https://www.uspreventiveservicestaskforce.org/.../latent...
https://downloads.aap.org/AAP/PDF/periodicity_schedule.pdf
https://dhss.alaska.gov/.../TB-School-Screening...
• @Alaska_DSS continues to test children at increased risk for TB as part of case investigations and community-wide screenings when communities with known TB activity occurs and why we also send out a strike team to work with local health officials in the case of an outbreak. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7637141/
• What can you do? Learn more at: https://www.cdc.gov/tb/topic/basics/risk.htm
• If you are at high risk for TB, make sure you talk to your health care provider to get tested.
• If you are infected, complete the full course to prevent drug-resistant TB.


Original source can be found here.
 Alerts Sign-up
Alerts Sign-up